Smelt Oven Induction Speedy Melting 6kg 8kg 10kg 15kg 20kg Manual Tilting Gold Smelting Furnace
Technical Parameters
| Model No. | HS-TF6 | HS-TF8 | HS-TF10 | HS-TF15 | HS-TF20 | HS-ATF30 | HS-ATF50 |
| Voltage | 380V 50Hz 3 phases | ||||||
| Power | 15KW | 20KW | 20KW | 25KW | 30KW | 30KW | 40KW |
| Max Temp | 1600℃ | ||||||
| Melting speed | 2 - 5 Min. | 3 - 6 Min. | 3 - 6 Mins | 3 - 6 Mins | 3 - 6 Mins | 6 - 10 Mins | 6 - 10 Mins |
| Temp Accuracy | ±1°C (optional) | ||||||
| Temperature detector | PID Temperature Control / Infrared pyrometer (Optional), extra cost added. | ||||||
| Capacity (Gold) | 6KG | 8KG | 10KG | 15KG | 20KG | 30KG | 50KG |
| Application | Gold K-Gold Sliver Cooper and other alloys (Platinum, Palladiu, Steel, Rhodium is customzied) | ||||||
| Heating method | Germany IGBT Induction heating technology | ||||||
| Cooling type | Water chiller(sold separately) or Running water (water pump) | ||||||
| Dimensions | 115*49*102cm | 125*65*135cm | |||||
| Net Weight | approx. 140kg | 150KG | 320KG | 450KG | |||
Product Display
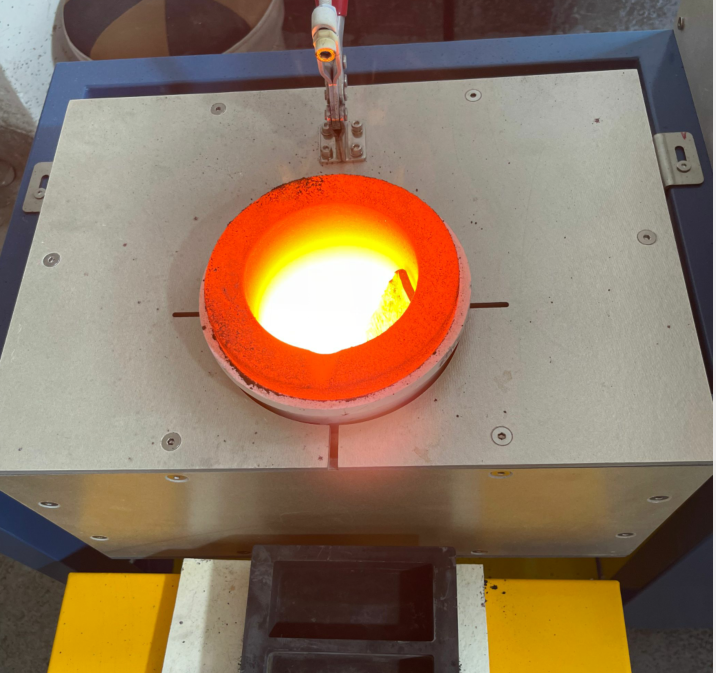




The Advantage of Tilting Induction Melting Furnaces in Precious Metals Smelting
1. Introduction
Precious metals, such as gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, have unique physical and chemical properties that make them highly valuable in various industries, including jewelry, electronics, and dentistry. The smelting process of precious metals requires high - precision and efficient equipment to ensure the quality of the final product and minimize material losses. Among different types of smelting furnaces, the tilting induction melting furnace has emerged as an excellent choice for precious metals smelting, offering several distinct advantages over other traditional smelting methods.
2. Working Principle of Tilting Induction Melting Furnaces
2.1 Induction Heating Principle
Induction heating is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) is passed through a coil (inductor), a changing magnetic field is generated around the coil. If a conductive metal charge is placed within this magnetic field, an induced electromotive force (emf) is generated in the metal. According to Ohm's law, this induced emf causes an induced current (eddy current) to flow within the metal. The resistance of the metal to the flow of these eddy currents results in the generation of heat, as described by the formula Q = I^{2}Rt, where Q is the heat generated, I is the current, R is the resistance, and t is the time. This heat is then used to melt the metal.
2.2 Tilting Mechanism
The tilting feature of the induction melting furnace is an additional mechanical design. The furnace body is mounted on a tilting mechanism that allows it to be tilted at a certain angle. This tilting function is crucial for the smooth pouring of the molten metal. When the metal is completely melted, the furnace can be tilted, and the molten metal can be poured into molds or other containers with precision, which is especially important for precious metals smelting where accurate pouring is necessary to avoid waste and ensure the quality of the cast products.
3. Advantages of Tilting Induction Melting Furnaces in Precious Metals Smelting
3.1 High - Purity Melting
3.1.1 Reduced Contamination
In precious metals smelting, maintaining high purity is of utmost importance. Traditional smelting methods, such as some fuel - fired furnaces, may introduce contaminants into the molten metal. For example, the combustion of fossil fuels in fuel - fired furnaces can release sulfur, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These substances can react with the precious metals during the smelting process, leading to the formation of impurities. In contrast, induction melting in a tilting furnace uses electromagnetic induction for heating, eliminating the need for combustion - based heat sources. As a result, there is significantly less risk of contamination from external sources, ensuring that the precious metals remain in a high - purity state during the melting process.
3.1.2 Precise Temperature Control
Precious metals often have specific melting points and require precise temperature control during smelting. Tilting induction melting furnaces are equipped with advanced temperature control systems. These systems can accurately sense the temperature of the molten metal and adjust the power input to the inductor accordingly. For instance, platinum has a melting point of around 1768 °C. With the precise temperature control of the tilting induction melting furnace, the temperature can be maintained within a very narrow range close to this melting point. This not only ensures complete melting of the metal but also prevents over - heating, which could potentially cause oxidation or other chemical changes that might reduce the purity of the precious metal.
3.2 Energy Efficiency
3.2.1 High - Frequency Induction Heating
Induction heating in tilting furnaces typically operates at high frequencies. High - frequency induction heating has a high conversion efficiency of electrical energy into heat energy. The electromagnetic field generated by the high - frequency current in the inductor can penetrate deep into the metal charge, causing the metal to heat up rapidly from within. This internal heating mechanism is much more efficient than external heating methods, such as radiant heating in some traditional furnaces. The rapid heating reduces the time required for melting the precious metals, which in turn reduces the overall energy consumption. For example, compared to some gas - fired furnaces, tilting induction melting furnaces can save up to 30 - 50% of energy during the smelting process of precious metals.
3.3.2 Smooth Pouring
The tilting function of the furnace plays a crucial role in enhancing productivity. Once the precious metal is melted, the smooth and controlled tilting of the furnace allows for quick and accurate pouring of the molten metal into molds. This reduces the time between melting and casting, minimizing the risk of solidification of the molten metal in the furnace and improving the overall efficiency of the production process. In addition, the precise pouring enabled by the tilting mechanism ensures that the molten metal fills the molds evenly, reducing the need for re - melting or post - processing due to incomplete or uneven casting.
3.4 Flexibility and Versatility
3.4.1 Different Precious Metal Smelting
Tilting induction melting furnaces can be used to smelt a variety of precious metals, including gold, silver, platinum, and palladium. Each of these precious metals has different melting points, chemical properties, and smelting requirements. The adjustable power and temperature control systems of the tilting induction melting furnace can be easily customized to meet the specific needs of different precious metals. For example, when smelting silver (melting point around 962 °C), the power and temperature settings can be adjusted accordingly, while for platinum (with a much higher melting point), the furnace can be set to operate at higher temperatures and power levels. This flexibility makes the tilting induction melting furnace a one - stop solution for smelting different precious metals in a single production facility.
3.4.2 Different Charge Sizes
These furnaces are available in a wide range of sizes, which allows for the smelting of different charge sizes of precious metals. Whether it is a small - scale jewelry production that requires melting a few grams of precious metals or a large - scale industrial smelting operation dealing with kilograms of precious metals, there is a suitable tilting induction melting furnace. Small - sized furnaces are often used in jewelry workshops, where precision and small - batch production are important. Large - scale industrial furnaces can handle large quantities of precious metals, meeting the demands of industries such as electronics manufacturing, which requires a large amount of high - purity precious metals for components production.
3.5 Safety and Environmental Friendliness
3.5.1 Safe Operation
Tilting induction melting furnaces are designed with multiple safety features. The electromagnetic induction heating system does not involve open flames, reducing the risk of fire and explosion compared to fuel - fired furnaces. In addition, the furnace is equipped with over - temperature protection, leakage protection, and other safety devices. For example, if the temperature of the furnace exceeds the set limit, the power supply will be automatically cut off to prevent damage to the equipment and potential safety hazards. The tilting mechanism also has safety locks and limit switches to ensure that the tilting operation is carried out smoothly and safely.
3.5.2 Reduced Emissions
Since tilting induction melting furnaces do not rely on combustion of fossil fuels, they produce significantly fewer emissions compared to traditional fuel - fired furnaces. They do not emit pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO_{2}), nitrogen oxides (NO_{x}), and particulate matter. This is not only beneficial for the environment but also for the health of the workers in the smelting facility. In addition, the energy - efficient operation of these furnaces means that less energy is consumed, which in turn reduces the carbon footprint associated with the smelting process, contributing to global efforts in combating climate change.
4. Case Studies and Industry Applications
4.1 Jewelry Industry
In the jewelry industry, the quality and purity of precious metals are of prime importance. Many high - end jewelry manufacturers use tilting induction melting furnaces to melt gold, silver, and platinum. For example, a well - known jewelry brand in Italy has reported that after switching to a tilting induction melting furnace, the quality of their gold jewelry has improved significantly. The high - purity melting ensures that the gold retains its luster and color for a long time. The fast melting speed and precise pouring also allow for more complex and detailed jewelry designs, as the molten metal can be accurately poured into intricate molds.
4.2 Electronics Industry
The electronics industry requires high - purity precious metals for the production of components such as connectors, circuit boards, and sensors. Palladium and platinum are often used in these applications due to their excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. A leading electronics manufacturer in Japan has adopted tilting induction melting furnaces for smelting these precious metals. The energy - efficient operation of the furnace has reduced their production costs, while the high - purity melting has improved the performance and reliability of their electronic products. The flexibility of the furnace to handle different charge sizes also meets the diverse production needs of the electronics industry, from small - scale prototype production to large - scale mass production.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, tilting induction melting furnaces offer numerous advantages for precious metals smelting. Their high - purity melting capabilities, energy - efficient operation, fast melting speed, flexibility, and safety features make them an ideal choice for industries that deal with precious metals. As the demand for high - quality precious metal products continues to grow in various industries such as jewelry, electronics, and dentistry, the use of tilting induction melting furnaces is expected to become even more widespread. Further research and development in this area may lead to even more advanced and efficient tilting induction melting furnace designs, further improving the efficiency and quality of precious metals smelting processes.
- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur