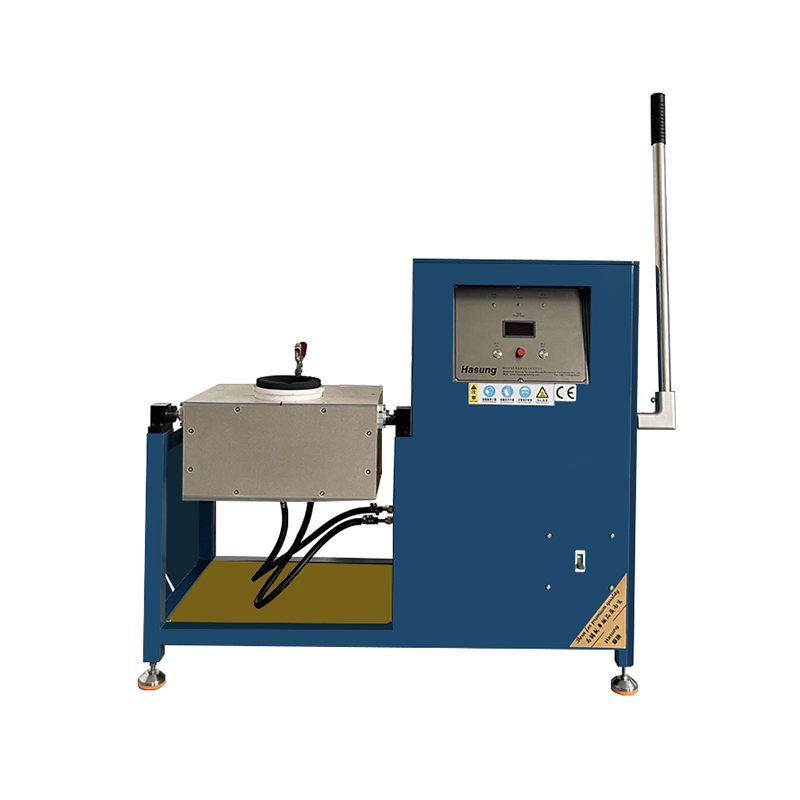
An induction melting furnace is an electric furnace that utilizes the induction heating effect of materials to heat or melt them. The main components of an induction furnace include sensors, furnace body, power supply, capacitors, and control system.
The main components of an induction furnace include sensors, furnace body, power supply, capacitors, and control system.
Under the action of alternating electromagnetic fields in an induction furnace, eddy currents are generated inside the material to achieve heating or melting effects. Under the stirring effect of this alternating magnetic field, the composition and temperature of the material in the furnace are relatively uniform. The forging heating temperature can reach 1250 ℃, and the melting temperature can reach 1650 ℃.
In addition to being able to heat or melt in the atmosphere, induction furnaces can also heat or melt in vacuum and protective atmospheres such as argon and neon to meet special quality requirements. Induction furnaces have outstanding advantages in permeating or melting soft magnetic alloys, high resistance alloys, platinum group alloys, heat-resistant, corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant alloys, and pure metals. Induction furnaces are usually divided into induction heating furnaces and smelting furnaces.
An electric furnace that uses the induced current generated by an induction coil to heat materials. If heating metal materials, place them in crucibles made of refractory materials. If heating non-metallic materials, place the materials in a graphite crucible. When the frequency of the alternating current is increased, the frequency of the induced current correspondingly increases, resulting in an increase in the amount of heat generated. The induction furnace heats quickly, has high temperatures, is easy to operate and control, and the materials are less contaminated during the heating process, ensuring product quality. Mainly used for melting special high-temperature materials, it can also be used as heating and control equipment for growing single crystals from melt.
Smelting furnaces are divided into two categories: cored induction furnaces and coreless induction furnaces.
A cored induction furnace has an iron core passing through the inductor and is powered by a power frequency power supply. It is mainly used for the melting and insulation of various metals such as cast iron, brass, bronze, zinc, etc., with an electrical efficiency of over 90%. It can utilize waste furnace materials, has low melting costs, and a maximum furnace capacity of 270 tons.
The coreless induction furnace has no iron core passing through the inductor, and is divided into power frequency induction furnace, triple frequency induction furnace, generator set medium frequency induction furnace, thyristor medium frequency induction furnace, and high-frequency induction furnace.
Supporting equipment
The complete equipment of the intermediate frequency induction furnace includes: power supply and electrical control part, furnace body part, transmission device, and water cooling system.
operational principle
When alternating current passes through the induction coil, an alternating magnetic field is generated around the coil, and the conductive material in the furnace generates an induced potential under the action of the alternating magnetic field. An electric current (eddy current) is formed at a certain depth on the surface of the furnace material, and the furnace material is heated and melted by eddy current.
(1) Fast heating speed, high production efficiency, less oxidation and decarbonization, saving material and forging die costs
Due to the principle of medium frequency induction heating being electromagnetic induction, its heat is generated within the workpiece itself. Ordinary workers can continue working on forging tasks in ten minutes after using a medium frequency electric furnace, without the need for professional furnace workers to perform furnace burning and sealing work in advance. Don’t worry about the waste of heated billets in the coal furnace caused by power outages or equipment malfunctions.
Due to the fast heating speed of this heating method, there is very little oxidation. Compared to coal burners, each ton of forgings saves at least 20-50 kilograms of steel raw materials, and its material utilization rate can reach 95%.
Due to the uniform heating and minimal temperature difference between the core and surface, this heating method greatly increases the service life of the forging die in forging, and the surface roughness of the forging is also less than 50um.
(2) Superior working environment, improved working environment and company image for workers, pollution-free, and low energy consumption
Compared with coal stoves, induction heating furnaces no longer expose workers to the baking and smoking of coal stoves under the scorching sun, meeting the various requirements of the environmental protection department. At the same time, they establish the company’s external image and the future development trend of the forging industry.
(3) Uniform heating, minimal temperature difference between the core and the surface, and high temperature control accuracy
Induction heating generates heat within the workpiece itself, resulting in uniform heating and minimal temperature difference between the core and surface. The application of temperature control system can achieve precise temperature control, improving product quality and qualification rate.
power frequency
Industrial frequency induction furnace is an induction furnace that uses industrial frequency current (50 or 60 Hz) as the power source. The industrial frequency induction furnace has developed into a widely used smelting equipment. It is mainly used as a melting furnace to smelt gray cast iron, malleable cast iron, ductile iron, and alloy cast iron. In addition, it is also used as a insulation furnace. Similarly, the power frequency induction furnace has replaced the cupola as a casting production aspect
Compared with the cupola, the industrial frequency induction furnace has many advantages, such as easy control of molten iron composition and temperature, low gas and inclusion content in castings, no environmental pollution, energy conservation, and improved working conditions. Therefore, in recent years, industrial frequency induction furnaces have developed rapidly.
The complete set of equipment for the industrial frequency induction furnace includes four major parts.
1. Furnace body part
The body of the industrial frequency induction furnace for smelting cast iron is composed of two induction furnaces (one for smelting and the other for backup), furnace cover, furnace frame, tilting furnace oil cylinder, and furnace cover moving opening and closing device.
2. Electrical part
The electrical part consists of power transformers, main contactors, balancing reactors, balancing capacitors, compensating capacitors, and electrical control consoles.
3. Water cooling system
The cooling water system includes capacitor cooling, inductor cooling, and flexible cable cooling. The cooling water system consists of a water pump, a circulating water tank or cooling tower, and pipeline valves.
4. Hydraulic system
The hydraulic system includes oil tank, oil pump, oil pump motor, hydraulic system pipelines and valves, and hydraulic operation platform.
Medium frequency
An induction furnace with a power supply frequency in the range of 150-10000 Hz is called an intermediate frequency induction furnace, and its main frequency is in the range of 150-2500 Hz. The domestic small frequency induction furnace power supply has three frequencies: 150, 1000, and 2500 Hz.
Intermediate frequency induction furnace is a special metallurgical equipment suitable for smelting high-quality steel and alloys. Compared with work rate induction furnaces, it has the following advantages:
(1) Fast melting speed and high production efficiency. The power density of medium frequency induction furnaces is high, and the power configuration per ton of steel is about 20-30% higher than that of industrial frequency induction furnaces. Therefore, under the same conditions, the melting speed of the intermediate frequency induction furnace is fast and the production efficiency is high.
(2) Strong adaptability and flexible use. Each furnace of the medium frequency induction furnace can completely discharge the molten steel, making it convenient to change the steel grade; However, the steel liquid in each furnace of the industrial frequency induction furnace is not allowed to be discharged completely, and a portion of the steel liquid must be reserved for the next furnace to start. Therefore, changing the steel grade is not convenient and is only suitable for smelting a single variety of steel.
(3) The electromagnetic stirring effect is good. Due to the electromagnetic force borne by the steel liquid being inversely proportional to the square root of the power supply frequency, the stirring force of the intermediate frequency power supply is smaller than that of the power frequency power supply. For the removal of impurities, uniform chemical composition, and uniform temperature in steel, the stirring effect of medium frequency power supply is relatively good. The excessive stirring force of the power frequency power supply increases the scouring force of the steel on the furnace lining, which not only reduces the refining effect but also reduces the lifespan of the crucible.
(4) Easy to start operation. Due to the skin effect of intermediate frequency current being much greater than that of power frequency current, there is no special requirement for the furnace material during start-up of the intermediate frequency induction furnace. After loading, it can be quickly heated and heated up; The industrial frequency induction furnace requires a specially made opening block (approximately half the height of the crucible, such as cast steel or cast iron) to start heating, and the heating rate is very slow. Therefore, under the condition of periodic operation, medium frequency induction furnaces are mostly used. Another advantage of easy starting is that it can save electricity during periodic operations.
The intermediate frequency furnace heating device has the advantages of small volume, light weight, high efficiency, excellent thermal processing quality, and favorable environment. It is rapidly phasing out coal fired furnaces, gas fired furnaces, oil fired furnaces, and ordinary resistance furnaces, and is a new generation of metal heating equipment.
Due to the above advantages, medium frequency induction furnaces have been widely used in the production of steel and alloys in recent years, and have also developed rapidly in the production of cast iron, especially in the casting workshop with periodic operations.

Post time: Mar-13-2024