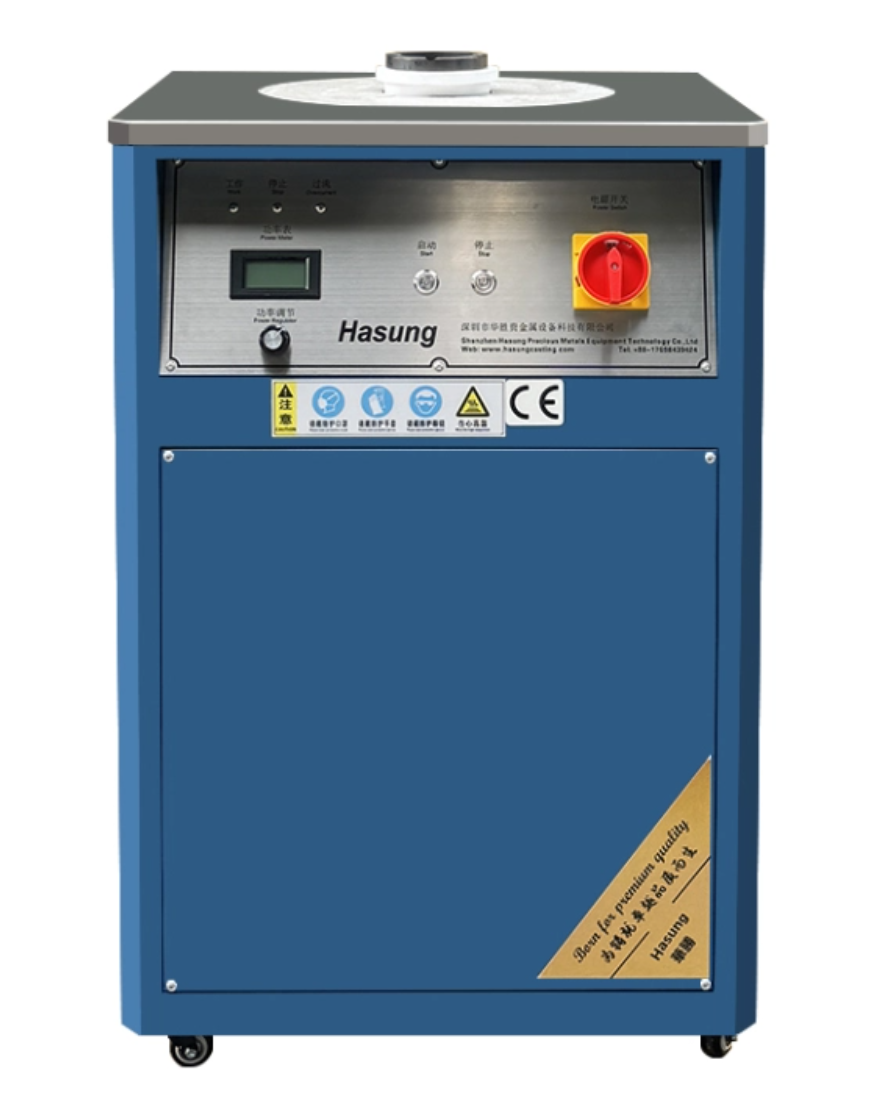
In the field of precious metal processing, casting efficiency is directly related to production costs, product delivery cycles, and the market competitiveness of enterprises. As one of the core equipment, the proper and efficient use of the melting machine can bring a qualitative leap to the entire casting process. The following will elaborate on the practical steps and key points of improving the casting efficiency of precious metals through a melting machine.
1. Equipment selection and preliminary preparation
(1) Accurate selection: Select the appropriate melting machine based on production scale, types and weights of precious metals commonly processed. In the early stage of small-scale workshops, if processing gold jewelry is the main focus and the processing capacity is not large, a small high-frequency gold melting machine with a power of 1-3kW can be selected. It heats up quickly, consumes relatively low energy, and can accurately control the melting of small doses of gold; Large jewelry factories, faced with mass casting of high melting point precious metals such as platinum and palladium, need to use medium frequency melting machines with a power of over 5kW or even higher to ensure that large capacity raw materials can be quickly and uniformly melted by heat, avoiding lengthy melting time due to insufficient power.
(2)Site layout: Install an independent, well ventilated, and dry space for the melting machine, away from flammable and explosive materials. On the one hand, good ventilation can timely discharge a small amount of harmful gases generated during the smelting of precious metals, ensuring the health of operators; On the other hand, a dry environment can prevent electrical components from getting damp and short circuiting, maintain stable equipment operation, and reduce downtime caused by faults. At the same time, plan the placement area for raw materials and tools reasonably to ensure smooth operation around the melting machine, such as arranging crucibles, molds, etc. in order of use for easy access and saving turnover time for material retrieval.
2. Optimization of operation process
(1) Raw material pretreatment: Before being put into the melting machine, carefully clean the precious metal raw materials to remove surface oil stains, impurities, oxides, etc. For example, wipe the gold block with a mild metal cleaner, then rinse with clean water and dry. This not only avoids impurities from entering the melt and affecting its purity, but also speeds up the melting process because pure metals have better thermal conductivity and more efficient heat transfer, allowing the melting process to be completed several minutes earlier. For bulk raw materials, if the size is large, appropriate crushing or cutting into small pieces can increase the contact area with the thermal field, which is also beneficial for accelerating melting.
(2) Precise temperature control: Set the melting machine temperature accurately based on the melting point of precious metals. If the melting point of silver is 961.78 ℃, the temperature should be precisely controlled between 960-970 ℃ during heating, which not only prevents silver from evaporating and wasting raw materials due to overheating, but also ensures that it can quickly melt into a uniform liquid state. Modern advanced melting machines often have intelligent temperature control systems that use high-precision sensors to monitor temperature in real time and adjust heating power through feedback; The operator should be familiar with the temperature control operation of the equipment, and make adjustments based on experience to ensure that the molten metal is in an ideal hot state throughout the entire process, reducing the ineffective time of repeated melting due to temperature fluctuations.
(3) Monitoring of the melting process: During the melting process, closely observe the state of the molten metal and check for any unmelted solids or bubbles through the observation window of the melting machine. Once abnormalities are detected, such as local overheating forming a hard shell that hinders melting, heating should be immediately paused, and the melt should be manually stirred or the heating mode adjusted; If there are bubbles, determine whether the raw material is damp or if there are slight cracks in the crucible that suck in gas, and solve them targetedly to avoid rework caused by defective products with air holes during casting, ensuring the success rate of single casting and improving overall efficiency.
3.Maintenance and personnel collaboration
(1) Daily maintenance: After each use, wait for the melting machine to cool down, clean the residual metal slag inside and outside the crucible, and use a soft bristled brush to clean the dust on the machine body, especially at the ventilation openings and electrical joints, to prevent dust accumulation from affecting heat dissipation and conductivity. Regularly inspect key parts such as heating elements, temperature control systems, and transmission components, replace vulnerable parts such as heating wires and thermocouples according to the equipment manual requirements, ensure that the equipment is in optimal operating condition at all times, and avoid sudden failures and shutdowns during production for maintenance.
(2)Personnel training and collaboration: Provide professional training to employees who operate the melting machine to deepen their understanding of equipment principles, operating points, and safety regulations. Skilled workers can predict melting problems and flexibly adjust parameters based on experience, while beginners may experience various situations that slow down progress due to improper operation. At the same time, personnel in each stage of casting work closely together. After the melting of gold is completed, the preparation of molds, pouring and other processes are seamlessly connected, minimizing the time from liquid precious metals to formed castings and fully utilizing the fast feeding advantage of the melting machine to achieve efficient mass production.
4.Technological upgrades and innovative applications
(1) Automation transformation: Introduce an automation control system to achieve linkage between the melting machine and subsequent casting processes. For example, when the molten metal reaches the set amount and state, the mold opening and pouring device is automatically triggered to accurately and quantitatively pour, reducing the time and heat loss of manual transfer of molten metal, reducing human error, improving product consistency, making the casting process compact and coherent, and significantly increasing efficiency.
(2) Application of new material crucible: Using new high-temperature resistant, thermally conductive, and corrosion-resistant crucible materials, such as graphite composite crucible, for melting platinum group metals. Compared to traditional crucibles, it has fast thermal conductivity, rapid heating, long lifespan, and reduces frequent replacement and shutdown of crucibles. It can also reduce the adhesion loss of precious metals on the crucible wall, comprehensively improving the efficiency of melting gold and subsequent casting from multiple aspects.
Through comprehensive measures such as equipment selection, operation optimization, maintenance, and technological innovation, precious metal casting enterprises are expected to significantly improve production efficiency, stand out in fierce market competition, and achieve cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and high-quality development by exploring the potential of the melting machine.
Post time: Jan-04-2025